
An example of raster overlay would be to divide the habitat of an endangered species into a grid, and then getting data for multiple factors that have an effect on the habitat and then creating a risk surface to illustrate what sections of the habitat need protecting most.

Raster overlay is often used to create risk surfaces, sustainability assessments, value assessments, and other procedures. These values then are mathematically merged together to create a new set of values for a single output layer. The separate sets of data are usually given numerical values. Raster overlay involves two or more different sets of data that derive from a common grid. It is important to note that these functions can change the original polygons and lines into new polygons and lines and their attributes. It can be derived as A subtract (A subtract B). It is most commonly used to trim one layer by a polygon represent an area of interest for the task. Clip contains the same overall extent as the intersection, but only retains the geometry and attributes of one of the input layers.It can be derived as A union (B subtract A). It is called "cover" because it looks like one layer is covering the other it is called "update" because its most common usage is when the covering layer represents recent changes that need to replace polygons in the original layer, such as new zoning districts. Cover, also known as Update, is similar to union in extent, but in the area where the two layers overlap, only the geometry and attributes of one of the layers is retained.
It can be derived as (A subtract B) union (A intersect B). Identity covers the extent of one of the two layers, with the geometery and attributes merged in the area where they overlap.It can be derived as either (A union B) subtract (A intersect B), or (A subtract B) union (B subtract A). Symmetric Difference, also known as Exclusive Or, which includes polygons that occur in one of the layers but not both.If a tool is not available, all of these could be derived from the first three in two or three steps. The remainder are used less often, and in a narrower range of applications. It is roughly analogous to AND NOT in logic and subtraction in arithmetic. Subtract, also known as Difference or Erase, where the result includes only those polygon parts that occur in one layer but not in another.
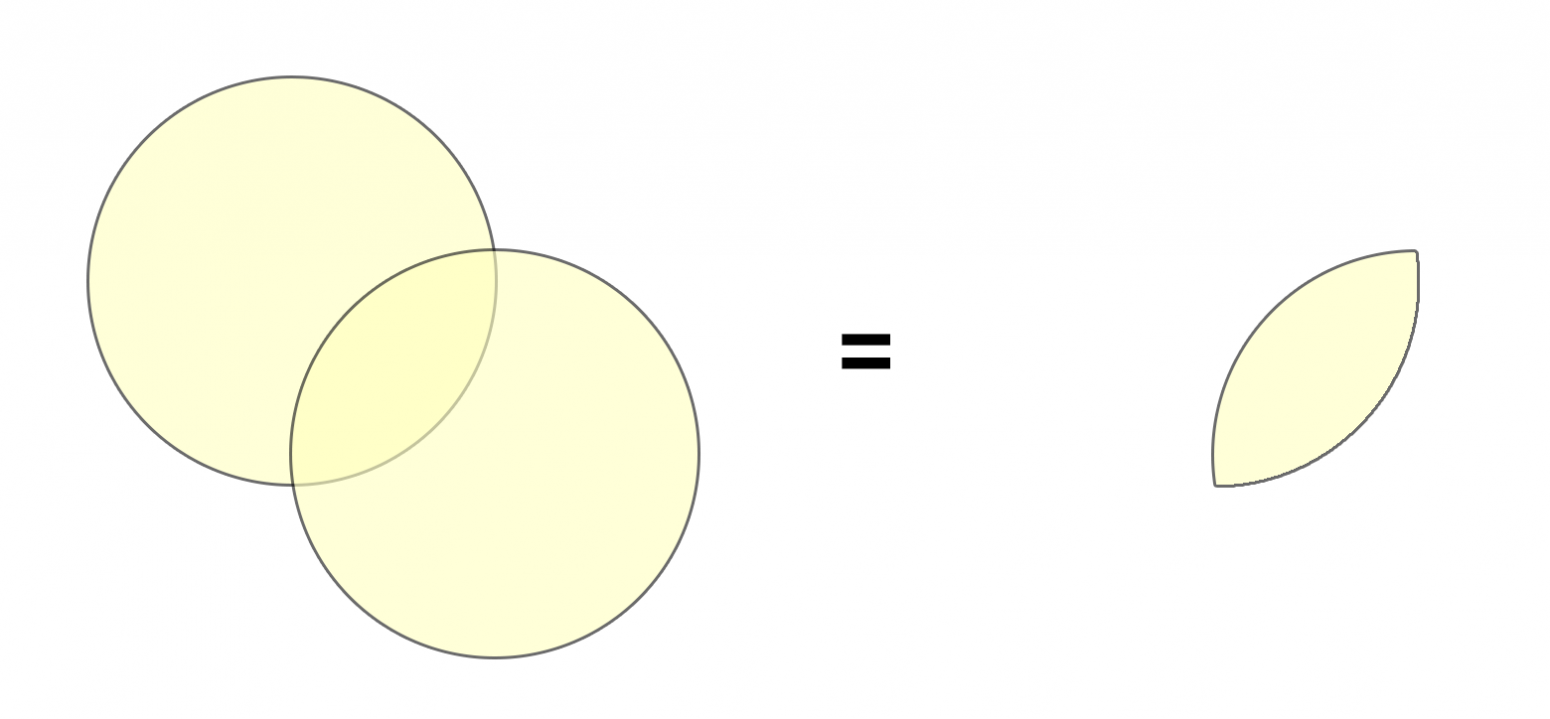
It is roughly analogous to OR in logic and addition in arithmetic. Different from identify in that individual layers are no longer identifiable.
GIS PERFORM INTERSECT WITH VECTOR AND RASTER SOFTWARE
Various GIS software packages offer a variety of polygon overlay tools, often with differing names.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
